Research
Researchers at CTER conduct research in collaboration with researchers or staff at other universities, local governments and NPOs within the following frameworks:
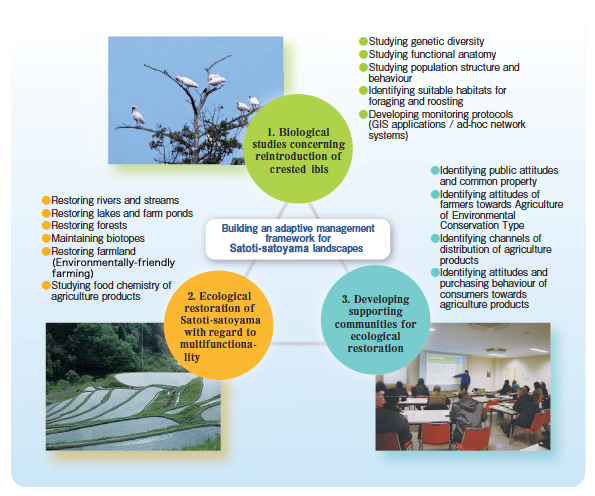
Framework I : Biological studies of reintroduced crested ibis♦Functional anatomy of crested ibis
♦Behavioural and population studies on crested ibis
♦Identifying suitable foraging and roosting habitats for crested ibis
♦Developing monitoring protocols for crested ibis
♦Evaluating the effectiveness of environmentally-friendly rice farming
♦Investigating wildlife-friendly managing practices for abandoned paddy fields
♦Evaluating the quality of agriculture products
♦Identifying attitudes and perceptions towards environmentally-friendly farming
♦Identifying consumer behaviour, attitudes and perceptions towards agriculture products
♦Assessing role and development processes of group farming
On the basis of the three frameworks, an adaptive management scenario will be proposed, and the scenario evaluated through both theoretical and practical approaches. In practice, Satoti-satoyama and supporting communities are expected to undergo dramatic changes through time so that the scenario will be amended to suit the then situation. The iterative study results are expected to provide scientific information to help inform environmental policy decisions being made by Sado City, Niigata Prefecture and/or Ministry of the Environment.
From May 2011, CTER initiated an Ecological Restoration project in the form of a donation programme by Sado City. In this programme, the members aim to develop cost-effective, environmentally-friendly farming practices and revitalization strategies for depopulated human communities on Sado Island. These studies are not only expected to play key roles in whole-island restoration but also in developing “Social-ecological Restoration”.

 Administration Office, Center for Transdisciplinary Research, Niigata University
Administration Office, Center for Transdisciplinary Research, Niigata University